publications
2024
Nicholson, R.M.‡, Levis, N.A., and Ragsdale, E.J. (2024). Genetic regulators of a resource polyphenism interact to couple predatory morphology and behaviour. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B 291:20240153. ‡Undergraduate author. [article] [data]
2023
Levis, N.A., Ragsdale, E.J. (2023). A histone demethylase links the loss of plasticity to nongenetic inheritance and morphological change. Nature Communications 14:8439. [article] [data]
Casasa, S., Katsougia, E., and Ragsdale, E.J. (2023). A Mediator subunit imparts robustness to a polyphenism decision. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 120:e2308816120. [article] [data]
2022
Ragsdale, E.J., Kanzaki, N., Yamashita, T., and Shinya, R. (2022). Tokorhabditis tauri n. sp. and T. atripennis n. sp. (Rhabditida: Rhabditidae), isolated from Onthophagus dung beetles (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) in the eastern USA and Japan. Journal of Nematology 54:e2022-0028. [article]
Harry, C.J.‡, Messar, S.M., and Ragsdale, E.J. (2022). Comparative reconstruction of the predatory feeding structures of the polyphenic nematode Pristionchus pacificus. Evolution & Development 24:16–36. ‡Undergraduate author. [article] [data]
Levis, N.A., and Ragsdale, E.J. (2022). Linking molecular mechanisms and evolutionary consequences of resource polyphenism. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience 16:805061. [article]
Sun, S., Theska, T., Witte, H., Ragsdale, E.J., and Sommer, R.J. (2022). The oscillating Mucin-type protein DPY-6 has a conserved role in nematode mouth and cuticle formation. Genetics 220:iyab233. [article]
2021
Kanzaki, N., Yamashita, T., Lee, J.S., Shih, P.Y., Ragsdale, E.J., and Shinya, R. (2021). Tokorhabditis n. gen. (Rhabditida, Rhabditidae), a comparative nematode model for extremophilic living. Scientific Reports 11:16470. [article]
Book chapter: Ledón-Rettig, C.C., and Ragsdale, E.J. (2021). Physiological mechanisms and the evolution of plasticity. In: Phenotypic plasticity & evolution: causes, consequences, controversies. Pfennig, D.W., ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, pp. 113–137. [book]
Casasa, S., Biddle, J.F., Koutsovoulos, G.D., and Ragsdale, E.J. (2021). Polyphenism of a novel trait integrated rapidly evolving genes into ancestrally plastic networks. Molecular Biology and Evolution 38:331–343. [article] [data]
2020
Biddle, J.F., and Ragsdale, E.J. (2020). Regulators of an ancient polyphenism evolved through episodic protein divergence and parallel gene radiations. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B 287:20192595. [article] [data]
2019
Bui, L.T., and Ragsdale, E.J. (2019).
Multiple plasticity regulators reveal targets specifying an induced
predatory form in nematodes. Molecular Biology and Evolution 36:2387–2399. [article] [data]
Ragsdale, E.J., Koutsovoulos, G., and Biddle, J.F. (2019). A draft genome for a species of Halicephalobus (Panagrolaimidae). Journal of Nematology 51:e2019-68. [article] [data]
2018
Ledón-Rettig, C.C., Moczek, A.P., and Ragsdale, E.J. (2018). Diplogastrellus nematodes are sexually transmitted mutualists that alter the bacterial and fungal communities of their beetle host. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 115:10696–10701. Featured in The Atlantic; also featured on Science Friday and Quirks & Quarks. [article] [data]
Bui, L.T., Ivers, N.A., and Ragsdale, E.J. (2018).
A sulfotransferase dosage-dependently regulates mouthpart polyphenism in the nematode Pristionchus pacificus. Nature Communications 9:4119. [article]
2017
Projecto-Garcia, J., Biddle, J.F., and
Ragsdale, E.J. (2017). Decoding the architecture and origins of
mechanisms for developmental polyphenism. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 47:1–8. [article]
Denver, D.R., Ragsdale, E.J., Thomas,
W.K., and Zasada, I.A. (2017). Introduction to nematode genome and
transcriptome announcements in the Journal of Nematology. Journal of Nematology 49:125–126. [article]
Herrmann, M., Kanzaki, N., Ragsdale, E.J., and Sommer, R.J. (2017). Redescription of four species of the genus Pristionchus (Nematoda: Diplogastridae) from the United States of America. Dumerilia 7:97–103.
Pereira, T.J., Qing, X., Chang, K.F.,
Mundo-Ocampo, M., Cares, J.E., Ragsdale, E.J., Nguyen, C.N., and
Baldwin, J.G. (2017). Phylogeny and biogeography of the genus Cephalenchus (Tylenchomorpha, Nematoda). Zoologica Scripta 46:506–520. [article]
2016
Ragsdale, E.J., and Ivers, N.A. (2016). Specialization of a polyphenism switch gene following serial duplications in Pristionchus nematodes. Evolution 70:2155–2166.
[article]
Kieninger, M.R., Ivers, N.A.,
Rödelsperger, C., Markov, G.V., Sommer, R.J., and Ragsdale, E.J. (2016).
The nuclear hormone receptor NHR-40 acts downstream of the sulfatase
EUD-1 as part of a developmental plasticity switch in Pristionchus. Current Biology 26:1–6.
[article]
Susoy, V., Herrmann, M., Kanzaki, N., Kruger, M., Nguyen, C.N., Rödelsperger,
C., Röseler, W., Weiler, C., Giblin-Davis, R.M., Ragsdale, E.J.*, and
Sommer, R.J.* (2016). Large-scale diversification without genetic
isolation in nematode symbionts of figs. Science Advances 2:e1501031. Recommended by Faculty of 1000. *Joint corresponding author. [article]
—Featured in: Phillips, P.C.
(2016). Evolution: Five heads are better than one. Current Biology 26:R275–R296. [article]
2015
Susoy, V., Ragsdale, E.J.*, Kanzaki, N.,
and Sommer, R.J.* (2015). Rapid diversification associated with a
macroevolutionary pulse of developmental plasticity. eLife 4:e05463. *Joint corresponding author. [article]
—Featured in: Nijhout, H.F. (2015). Evolution: To plasticity and back again. eLife 4:e06995. [article]
Book chapter: Ragsdale, E.J. (2015). Mouth dimorphism and the evolution of novelty and diversity. In: Pristionchus pacificus: a nematode model for comparative and evolutionary biology. Sommer, R.J., ed. Leiden: Brill, pp. 301–329. [book]
Book chapter: Ragsdale, E.J., Kanzaki, N., and Herrmann, M. (2015). Taxonomy and natural history: the genus Pristionchus. In: Pristionchus pacificus: a nematode model for comparative and evolutionary biology. Sommer, R.J., ed. Leiden: Brill, pp. 77–120. [book]
Kanzaki, N., Giblin-Davis, R.M., and Ragsdale, E.J. (2015). Allodiplogaster josephi n. sp. and A. seani n. sp. (Nematoda: Diplogastridae), associates of soil-dwelling bees in the eastern USA. Nematology 17:831–863. [article]
2014
Kanzaki, N., Ragsdale, E.J., and Giblin-Davis, R.M. (2014). Revision of the paraphyletic genus Koerneria Meyl, 1960 and resurrection of two other genera of Diplogastridae (Nematoda). ZooKeys 442:17–30. [article]
Serobyan, V., Ragsdale, E.J., and Sommer, R.J. (2014).
Adaptive value of a predatory mouth-form in a dimorphic nematode. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B 281:20141334. [article]
Ragsdale, E.J., Kanzaki, N., and Sommer, R.J. (2014). Levipalatum texanum n. gen., n. sp. (Nematoda: Diplogastridae), an androdioecious species from the south-eastern USA. Nematology 16:695–709. [article]
Kanzaki, N., Ragsdale, E.J., Herrmann, M., and Sommer, R.J. (2014). Two new and two recharacterized species from a radiation of Pristionchus (Nematoda: Diplogastridae) in Europe. Journal of Nematology 46:60–74. [article]
Kanzaki, N., Ragsdale, E.J., Susoy, V., and Sommer, R.J. (2014). Leptojacobus dorci n. gen., n. sp. (Nematoda: Diplogastridae), an associate of Dorcus stag beetles (Coleoptera: Lucanidae). Journal of Nematology 46:50–59. Cover feature. [article]
2013
Ragsdale, E.J., Müller, M.R., Rödelsperger, C., and Sommer,
R.J. (2013). A developmental switch coupled to the evolution of
plasticity acts through a sulfatase. Cell 155:922–933. [article]
—Featured in: Hartenstein, V., and Jacobs, D. (2013). Developmental plasticity, straight from the worm's mouth. Cell 155:742–743. [article]
Serobyan, V., Ragsdale, E.J., Müller, M.R., and Sommer, R.J. (2013). Feeding plasticity in the nematode Pristionchus pacificus is influenced by sex and social context and is linked to developmental speed. Evolution & Development 15:161–170. Cover feature. [article]
Ragsdale, E.J., Kanzaki, N., Röseler, W., Herrmann, M., and Sommer, R.J. (2013). Three new species of Pristionchus
(Nematoda: Diplogastridae) show morphological divergence through
evolutionary intermediates of a novel feeding-structure polymorphism. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 168:671–698. [article]
Herrmann, M., Ragsdale, E.J., Kanzaki, N., and Sommer, R.J. (2013). Sudhausia aristotokia n. gen., n. sp. and S. crassa n. gen., n. sp. (Nematoda: Diplogastridae): viviparous new species with precocious gonad development. Nematology 15:1001–1020. [article]
Kanzaki, N., Ragsdale, E.J., Herrmann, M., Susoy, V., and
Sommer, R.J. (2013). Two androdioecious and one dioecious new species
of Pristionchus (Nematoda: Diplogastridae): new reference points for the evolution of reproductive mode. Journal of Nematology 45:172–194. [article]
Kanzaki, N., Ragsdale, E.J., Herrmann, M., Röseler, W., and Sommer, R.J. (2013). Two new species of Pristionchus (Nematoda: Diplogastridae) support the biogeographic importance of Japan for the evolution of the genus Pristionchus and the model system P. pacificus. Zoological Science 30:680–692. [article]
Kanzaki, N., Ragsdale, E.J., Herrmann, M., Röseler, W., and Sommer, R.J. (2013). Pristionchus bucculentus n. sp. (Rhabditida: Diplogastridae) isolated from a shining mushroom beetle (Coleoptera: Scaphidiidae) in Hokkaido, Japan. Journal of Nematology 45:78–86. [article]
2012
Bose, N., Ogawa, A., von Reuss, S.H., Yim, J.J.,
Ragsdale, E.J., Sommer, R.J., and Schroeder, F.C. (2012). Complex
small-molecule architectures regulate phenotypic plasticity in a
nematode. Angewandte Chemie 51:12438–12443. Frontispiece feature. [article]
Kanzaki, N., Ragsdale, E.J., Herrmann, M., Mayer, W.E., Tanaka, R., and Sommer, R.J. (2012). Parapristionchus giblindavisi n. gen., n. sp. (Rhabditida: Diplogastridae) isolated from stag beetles (Coleoptera: Lucanidae) in Japan. Nematology 14:933–947. Cover feature. [article]
Kanzaki, N., Ragsdale, E.J., Herrmann, M., and Sommer, R.J. (2012). Two new species of Pristionchus (Rhabditida: Diplogastridae): P. fissidentatus n. sp. from Nepal and La Réunion Island and P. elegans n. sp. from Japan. Journal of Nematology 44:80–91. Cover feature. [article]
Kanzaki, N., Ragsdale, E.J., Herrmann, M., Mayer, W.E., and Sommer, R.J. (2012). Description of three Pristionchus species (Nematoda: Diplogastridae) from Japan that form a cryptic species complex with the model organism P. pacificus. Zoological Science 29:403–417. Cover feature. [article]
2011
Ragsdale, E.J., Ngo, P. T., Crum, J., Ellisman, M.H., and Baldwin, J.G. (2011). Reconstruction of the pharyngeal corpus of Aphelenchus avenae (Nematoda: Tylenchomorpha), with implications for phylogenetic congruence. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 161:1–30. [article]
Ragsdale, E.J., Mundo-Ocampo, M., Bumbarger, D.J., and Baldwin, J.G. (2011). Cervidellus sonorensis n. sp. (Nematoda: Cephalobidae) from the desert of Anza-Borrego, CA, USA. Nematology 13:607–617. Cover feature. [article]
2010
Ragsdale, E.J., and Baldwin, J.G. (2010). Resolving
phylogenetic incongruence to articulate homology and phenotypic
evolution: a case study from Nematoda. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B 277:1299–1307. [article]
Giblin-Davis, R.M., Kanzaki, N., De Ley, P.,
Williams, D.S., Schierenberg, E., Ragsdale, E.J., Zeng Y.-S., and
Center, B.J. (2010). Ultrastructure and life history of Myolaimus byersi n. sp. (Myolaimina: Myolaimidae), a phoretic associate of the crane fly Limonia schwarzi (Alexander) (Limoniidae) in Florida. Nematology 12:519–542. [article]
2009 and earlier
Ragsdale, E.J., Ngo, P.T., Crum, J., Ellisman, M.H., and
Baldwin, J.G. (2009). Comparative, three-dimensional anterior
sensory reconstruction of Aphelenchus avenae (Nematoda: Tylenchomorpha). Journal of Comparative Neurology 517:616–632. [article]
Subbotin, S.A., Ragsdale, E.J., Mullens, T.,
Roberts, P.A., Mundo-Ocampo, M., and Baldwin, J.G. (2008). A
phylogenetic framework for root lesion nematodes of the genus Pratylenchus (Nematoda): evidence from 18S and D2-D3 expansion segments of 28S ribosomal RNA genes and morphological characters. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 48:491–505. [article]
Ragsdale, E.J., Crum, J., Ellisman, M.H., and Baldwin, J.G.
(2008). Three-dimensional reconstruction of the stomatostylet and
anterior epidermis in the nematode Aphelenchus avenae (Nematoda: Aphelenchidae) with implications for the evolution of plant parasitism. Journal of Morphology 269:1181–1196. [article]
Baldwin, J.G., Ragsdale, E.J., and Bumbarger, D. (2004).
Revised hypotheses for phylogenetic homology of the stomatostylet in
tylenchid nematodes. Nematology 6:623–632. [article]
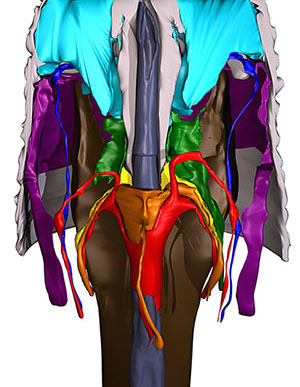
Reconstruction of piercing mouthparts in Aphelenchus avenae

